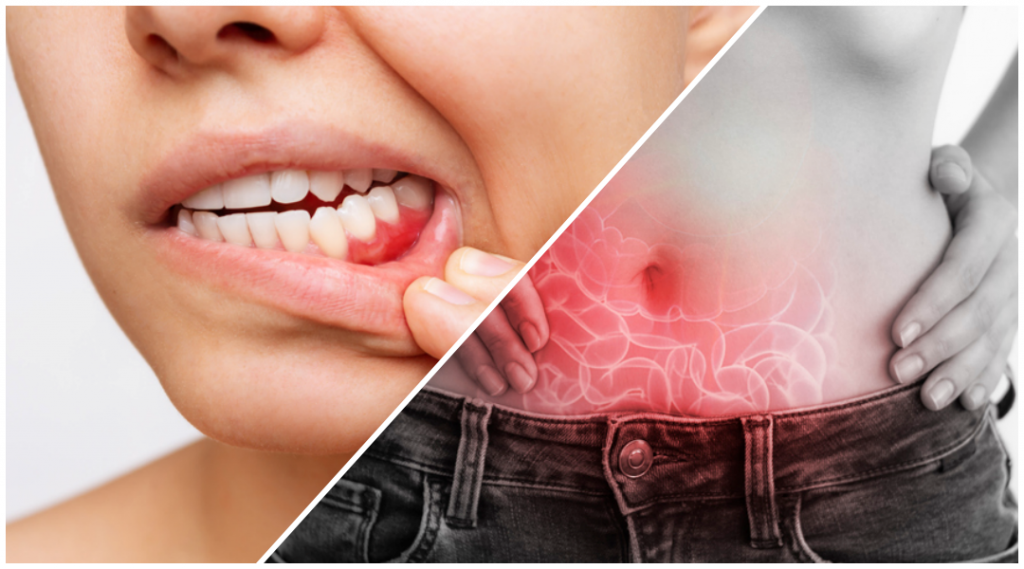
In the intricate tapestry of our health, the link between oral well-being and systemic health is a topic gaining increasing attention. Beyond the routine dental check-ups and charming smiles, recent research has unveiled a fascinating connection between gum disease and gastrointestinal issues. Join us on a journey ‘Beyond the Smile’ to explore the intriguing relationship between our gums and gut health.
While gum disease (periodontal disease) primarily affects the gums and teeth-supporting structures, there is evidence suggesting a potential link between gum disease and certain gastrointestinal (GI) issues. The connection is thought to be related to the inflammatory nature of both conditions.
Research has indicated that the inflammation associated with gum disease might contribute to systemic inflammation. In turn, this could affect other parts of the body, including the gastrointestinal tract. Chronic inflammation is a common factor in various health conditions, including some GI disorders.
Some studies have explored potential associations between gum disease and conditions like inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), Crohn’s disease, and ulcerative colitis. While the evidence is not conclusive, there seems to be a link between oral health and certain GI conditions. However, it’s important to note that correlation does not imply causation. More research is needed to establish the exact nature of these relationships.
Maintaining good oral hygiene, including regular dental check-ups and cleanings, is essential not only for oral health but potentially for overall well-being. If you have concerns about the possible connections between gum disease and GI issues, discuss them with your periodontist and doctor. They can provide more personalized information based on your specific health situation.
How Gum Disease Can Potentially Affect the Gut
When the gums are inflamed, the body’s immune response is triggered, releasing inflammatory molecules. These inflammatory substances can enter the bloodstream and circulate throughout the body. These substances can potentially affect distant organs and tissues, including the gastrointestinal (GI) tract.
The gut is sensitive to systemic inflammation, and chronic inflammation is a known factor in various gastrointestinal conditions. While the exact mechanisms are not fully understood, it’s hypothesized that the inflammatory mediators originating from the oral cavity may contribute to or exacerbate inflammation in the gut. This could be particularly relevant in conditions like inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), Crohn’s disease, or ulcerative colitis, where inflammation plays a central role.
Moreover, some studies suggest that the bacteria associated with gum disease might also play a role in the development or exacerbation of certain GI conditions. The oral microbiome and gut microbiome are interconnected. Disruptions in the balance of bacteria in one area may influence the other.
Indicators of Possible Gum Disease
Gum disease can manifest in various stages, and the signs and symptoms may vary. It’s important to be aware of these indicators and seek professional dental advice if you notice any of the following signs:
- Bleeding Gums: One of the early signs of gum disease is bleeding gums, especially during or after brushing and flossing.
- Swollen or Red Gums: Healthy gums should be pink and firm. If your gums appear red, swollen, or tender, it could be a sign of inflammation.
- Persistent Bad Breath: Chronic bad breath, also known as halitosis, can be associated with gum disease. It is often caused by the presence of bacteria in the mouth.
- Receding Gums: As gum disease progresses, the gums may start to pull away from the teeth, leading to gum recession. This can make the teeth appear longer.
- Changes in Tooth Alignment: The shifting or loosening of teeth without an apparent cause can be a symptom of advanced gum disease affecting the bone supporting the teeth.
- Pain or Discomfort: Discomfort, pain, or sensitivity in the gums may indicate an issue, especially if it persists.
- Pus Between Teeth and Gums: The presence of pus, which may appear as a yellowish or greenish discharge, could be a sign of an infection associated with gum disease.
- Changes in the Fit of Dentures: If you wear dentures, you may notice changes in how they fit if your gums and underlying bones are affected by gum disease.
It’s important to note that gum disease can progress with few noticeable symptoms in its early stages. Therefore, regular dental check-ups are crucial for early detection and intervention. If you observe any of these signs, it’s advisable to consult with a periodontist for a comprehensive examination and treatment. Practicing good oral hygiene, including regular brushing, flossing, and professional dental cleanings, can help prevent and manage gum disease.
GET IN TOUCH
